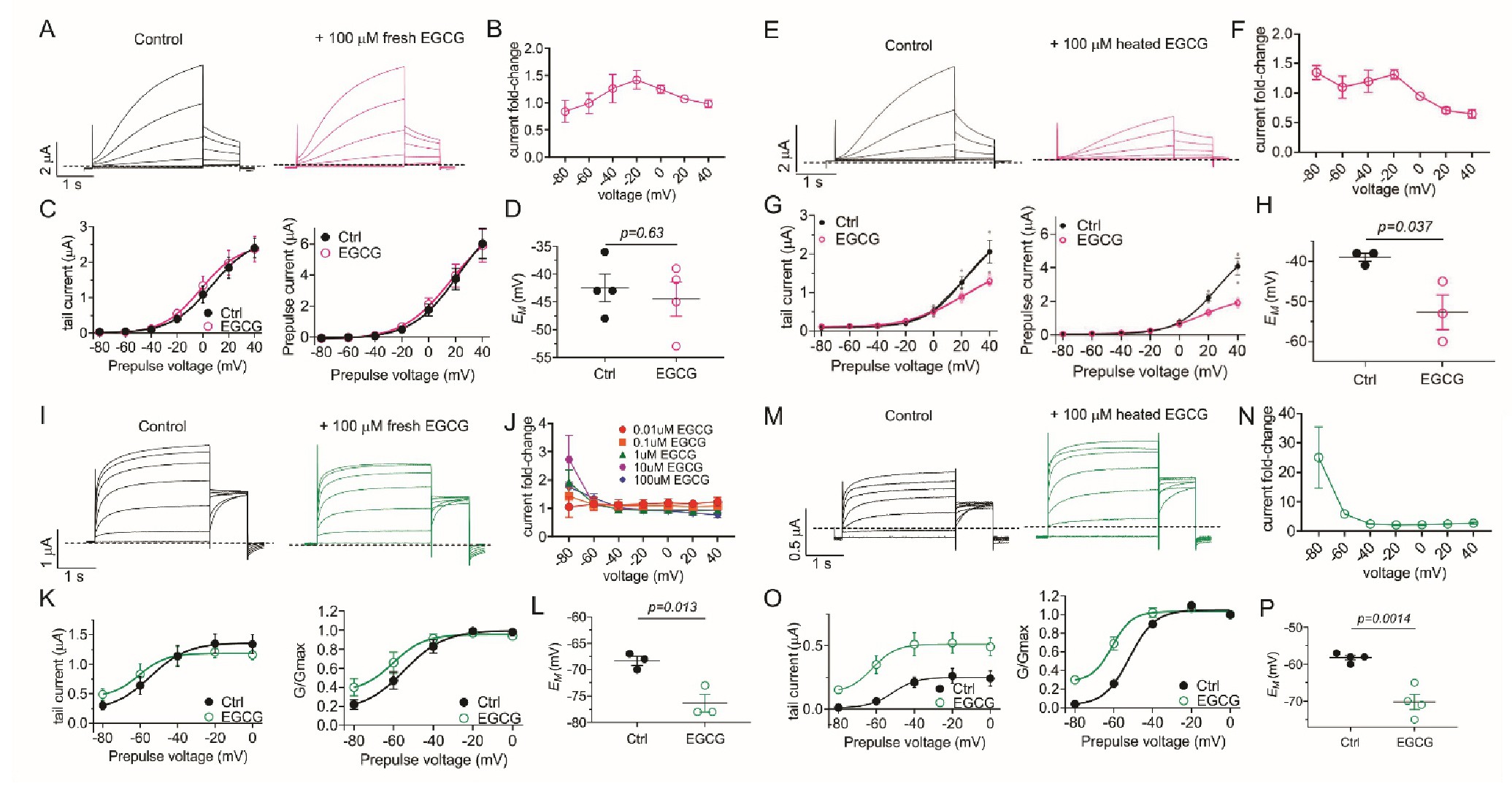
Fig. 8. Heating EGCG enables KCNQ1/E1 inhibition and KCNQ5 activation. All error bars indicate SEM. A: Mean KCNQ1/E1 traces in the absence (Control) and presence of 100 ÁM fresh EGCG (n = 4). B: KCNQ1/E1 tail current fold-change versus voltage for traces as in A (n = 4). C: Left, mean tail current; right, mean prepulse current versus prepulse voltage for traces as in A (n = 4). D: Scatter plot of unclamped membrane potential (EM) for cells as in A (n = 4). Statistical analyses by two-way ANOVA. E: Mean KCNQ1/E1 traces in the absence (Control) and presence of 100 ÁM heated EGCG (n = 4). F: KCNQ1/E1 tail current fold-change versus voltage for traces as in E (n = 4). G: Left, mean tail current; right, mean prepulse current versus prepulse voltage for traces as in E (n = 4). H: Scatter plot of unclamped membrane potential (EM) for cells as in E (n = 4). Statistical analyses by two-way ANOVA. I: Mean KCNQ5 traces in the absence (Control) and presence of 100 ÁM fresh EGCG (n = 4). J: KCNQ5 tail current fold-change versus voltage for traces as in I, for a range of fresh EGCG concentrations (n = 4). K: Left, mean tail current; right, mean normalized tail current (G/Gmax) versus prepulse voltage for traces as in I (n = 4). L: Scatter plot of unclamped membrane potential (EM) for cells as in I (n = 4). Statistical analyses by two-way ANOVA. M: Mean KCNQ5 traces in the absence (Control) and presence of 100 ÁM heated EGCG (n = 4). N: KCNQ5 tail current fold-change versus voltage for traces as in M (n = 4). O: Left, mean tail current; right, mean normalized tail current (G/Gmax) versus prepulse voltage for traces as in M (n = 4). P: Scatter plot of unclamped membrane potential (EM) for cells as in M (n = 4). Statistical analyses by two-way ANOVA.